Product Description
Product Description:
1.Flexspline is a hollow flanging standard cylinder structure.
2.There is a large-diameter hollow shaft hole in the middle of the cam of the wave generator. The internal design of the reducer has a support bearing.
3.It has a fully sealed structure and is easy to install. It is very suitable for the occasions where the wire needs to be threaded from the center of the reducer.
Advantages:
The first:High precision,high torque
The second:dedicated technical personnel can be on-the-go to provide design solutions
The third:Factory direct sales fine workmanship durable quality assurance
The fourth:Product quality issues have a one-year warranty time, can be returned for replacement or repair
Company profile:
HangZhou CHINAMFG Technology Co., Ltd. established in 2014, is committed to the R & D plant of high-precision transmission components. At present, the annual production capacity can reach 45000 sets of harmonic reducers. We firmly believe in quality first. All links from raw materials to finished products are strictly supervised and controlled, which provides a CHINAMFG foundation for product quality. Our products are sold all over the country and abroad.
The harmonic reducer and other high-precision transmission components were independently developed by the company. Our company spends 20% of its sales every year on the research and development of new technologies in the industry. There are 5 people in R & D.
Our advantage is as below:
1.7 years of marketing experience
2. 5-person R & D team to provide you with technical support
3. It is sold at home and abroad and exported to Turkey and Ireland
4. The product quality is guaranteed with a one-year warranty
5. Products can be customized
Strength factory:
Our plant has an entire campus The number of workshops is around 300 Whether it’s from the production of raw materials and the procurement of raw materials to the inspection of finished products, we’re doing it ourselves. There is a complete production system
HST-III Parameter:
| Model | Speed ratio | Enter the rated torque at 2000r/min | Allowed CHINAMFG torque at start stop | The allowable maximum of the average load torque | Maximum torque is allowed in an instant | Allow the maximum speed to be entered | Average input speed is allowed | Back gap | design life | ||||
| NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | r / min | r / min | Arc sec | Hour | ||
| 14 | 50 | 6.2 | 0.6 | 20.7 | 2.1 | 7.9 | 0.7 | 40.3 | 4.1 | 7000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 10000 |
| 80 | 9 | 0.9 | 27 | 2.7 | 12.7 | 1.3 | 54.1 | 5.5 | |||||
| 100 | 9 | 0.9 | 32 | 3.3 | 12.7 | 1.3 | 62.1 | 6.3 | |||||
| 17 | 50 | 18.4 | 1.9 | 39 | 4 | 29.9 | 3 | 80.5 | 8.2 | 6500 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 25.3 | 2.6 | 49.5 | 5 | 31 | 3.2 | 100.1 | 10.2 | |||||
| 100 | 27.6 | 2.8 | 62 | 6.3 | 45 | 4.6 | 124.2 | 12.7 | |||||
| 20 | 50 | 28.8 | 2.9 | 64.4 | 6.6 | 39 | 4 | 112.7 | 11.5 | 5600 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 39.1 | 4 | 85 | 8.8 | 54 | 5.5 | 146.1 | 14.9 | |||||
| 100 | 46 | 4.7 | 94.3 | 9.6 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 120 | 46 | 4.7 | 100 | 10.2 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 160 | 46 | 4.7 | 100 | 10.2 | 56 | 5.8 | 169.1 | 17.2 | |||||
| 25 | 50 | 44.9 | 4.6 | 113 | 11.5 | 63 | 6.5 | 213.9 | 21.8 | 4800 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 72.5 | 7.4 | 158 | 16.1 | 100 | 10.2 | 293.3 | 29.9 | |||||
| 100 | 77.1 | 7.9 | 181 | 18.4 | 124 | 12.7 | 326.6 | 33.3 | |||||
| 120 | 77.1 | 7.9 | 192 | 19.6 | 124 | 12.7 | 349.6 | 35.6 | |||||
| 32 | 50 | 87.4 | 8.9 | 248 | 25.3 | 124 | 12.7 | 439 | 44.8 | 4000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
| 80 | 135.7 | 13.8 | 350 | 35.6 | 192 | 19.6 | 653 | 66.6 | |||||
| 100 | 157.6 | 16.1 | 383 | 39.1 | 248 | 25.3 | 744 | 75.9 | |||||
| 40 | 100 | 308 | 37.2 | 660 | 67 | 432 | 44 | 1232 | 126.7 | 4000 | 3000 | ≤30 | 15000 |
HSG Parameter:
| Model | Speed ratio | Enter the rated torque at 2000r/min | Allowed CHINAMFG torque at start stop | The allowable maximum of the average load torque | Maximum torque is allowed in an instant | Allow the maximum speed to be entered | Average input speed is allowed | Back gap | design life | ||||
| NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | NM | kgfm | r / min | r / min | Arc sec | Hour | ||
| 14 | 50 | 7 | 0.7 | 23 | 2.3 | 9 | 0.9 | 46 | 4.7 | 14000 | 8500 | ≤20 | 15000 |
| 80 | 10 | 1 | 30 | 3.1 | 14 | 1.4 | 61 | 6.2 | |||||
| 100 | 10 | 1 | 36 | 3.7 | 14 | 1.4 | 70 | 7.2 | |||||
| 17 | 50 | 21 | 2.1 | 44 | 4.5 | 34 | 3.4 | 91 | 9 | 10000 | 7300 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 29 | 2.9 | 56 | 5.7 | 35 | 3.6 | 113 | 12 | |||||
| 100 | 31 | 3.2 | 70 | 7.2 | 51 | 5.2 | 143 | 15 | |||||
| 20 | 50 | 33 | 3.3 | 73 | 7.4 | 44 | 4.5 | 127 | 13 | 10000 | 6500 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 44 | 4.5 | 96 | 9.8 | 61 | 6.2 | 165 | 17 | |||||
| 100 | 52 | 5.3 | 107 | 10.9 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 120 | 52 | 5.3 | 113 | 11.5 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 160 | 52 | 5.3 | 120 | 12.2 | 64 | 6.5 | 191 | 20 | |||||
| 25 | 50 | 51 | 5.2 | 127 | 13 | 72 | 7.3 | 242 | 25 | 7500 | 5600 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 82 | 8.4 | 178 | 18 | 113 | 12 | 332 | 34 | |||||
| 100 | 87 | 8.9 | 204 | 21 | 140 | 14 | 369 | 38 | |||||
| 120 | 87 | 8.9 | 217 | 22 | 140 | 14 | 395 | 40 | |||||
| 32 | 50 | 99 | 10 | 281 | 29 | 140 | 14 | 497 | 51 | 7000 | 4800 | ≤20 | 20000 |
| 80 | 153 | 16 | 395 | 40 | 217 | 22 | 738 | 75 | |||||
| 100 | 178 | 18 | 433 | 44 | 281 | 29 | 841 | 86 | |||||
| 40 | 100 | 345 | 35 | 738 | 75 | 484 | 49 | 1400 | 143 | 5600 | 4000 | ≤20 | 20000 |
Exhibition:
Application case:
FQA:
Q: What should I provide when I choose gearbox/speed reducer?
A: The best way is to provide the motor drawing with parameter. Our engineer will check and recommend the most suitable gearbox model for your refer.
Or you can also provide below specification as well:
1) Type, model and torque.
2) Ratio or output speed
3) Working condition and connection method
4) Quality and installed machine name
5) Input mode and input speed
6) Motor brand model or flange and motor shaft size
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | 90 Degree |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Gear Shape: | Cylindrical Gear |
| Step: | Single-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How are servo motors used in CNC machines and other precision machining equipment?
Servo motors play a crucial role in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and other precision machining equipment. They provide precise and dynamic control over the movement of various axes, enabling high-accuracy positioning, rapid speed changes, and smooth motion profiles. Here’s a detailed explanation of how servo motors are used in CNC machines and precision machining equipment:
1. Axis Control:
CNC machines typically have multiple axes, such as X, Y, and Z for linear movements, as well as rotary axes for rotational movements. Servo motors are employed to drive each axis, converting electrical signals from the CNC controller into mechanical motion. The position, velocity, and acceleration of the servo motors are precisely controlled to achieve accurate and repeatable positioning of the machine’s tool or workpiece.
2. Feedback and Closed-Loop Control:
Servo motors in CNC machines are equipped with feedback devices, such as encoders or resolvers, to provide real-time information about the motor’s actual position. This feedback is used in a closed-loop control system, where the CNC controller continuously compares the desired position with the actual position and adjusts the motor’s control signals accordingly. This closed-loop control ensures accurate positioning and compensates for any errors, such as mechanical backlash or load variations.
3. Rapid and Precise Speed Changes:
Servo motors offer excellent dynamic response, allowing CNC machines to achieve rapid and precise speed changes during machining operations. By adjusting the control signals to the servo motors, the CNC controller can smoothly accelerate or decelerate the machine’s axes, resulting in efficient machining processes and reduced cycle times.
4. Contouring and Path Tracing:
CNC machines often perform complex machining tasks, such as contouring or following intricate paths. Servo motors enable precise path tracing by accurately controlling the position and velocity of the machine’s tool along the programmed path. This capability is crucial for producing intricate shapes, smooth curves, and intricate details with high precision.
5. Spindle Control:
In addition to axis control, servo motors are also used to control the spindle in CNC machines. The spindle motor, typically a servo motor, rotates the cutting tool or workpiece at the desired speed. Servo control ensures precise speed and torque control, allowing for optimal cutting conditions and surface finish quality.
6. Tool Changers and Automatic Tool Compensation:
CNC machines often feature automatic tool changers to switch between different cutting tools during machining operations. Servo motors are utilized to precisely position the tool changer mechanism, enabling quick and accurate tool changes. Additionally, servo motors can be used for automatic tool compensation, adjusting the tool’s position or orientation to compensate for wear, tool length variations, or tool offsets.
7. Synchronized Motion and Multi-Axis Coordination:
Servo motors enable synchronized motion and coordination between multiple axes in CNC machines. By precisely controlling the servo motors on different axes, complex machining operations involving simultaneous movements can be achieved. This capability is vital for tasks such as 3D contouring, thread cutting, and multi-axis machining.
In summary, servo motors are integral components of CNC machines and precision machining equipment. They provide accurate and dynamic control over the machine’s axes, enabling high-precision positioning, rapid speed changes, contouring, spindle control, tool changers, and multi-axis coordination. The combination of servo motor technology and CNC control systems allows for precise, efficient, and versatile machining operations in various industries.

Are there different types of servo motors, and how do they differ?
Yes, there are different types of servo motors available, each with its own characteristics and applications. The variations among servo motors can be attributed to factors such as construction, control mechanisms, power requirements, and performance specifications. Let’s explore some of the common types of servo motors and how they differ:
1. DC Servo Motors:
DC servo motors are widely used in various applications. They consist of a DC motor combined with a feedback control system. The control system typically includes a position or velocity feedback sensor, such as an encoder or a resolver. DC servo motors offer good speed and torque control and are often employed in robotics, automation, and hobbyist projects. They can be operated with a separate motor driver or integrated into servo motor units with built-in control electronics.
2. AC Servo Motors:
AC servo motors are designed for high-performance applications that require precise control and fast response times. They are typically three-phase motors and are driven by sinusoidal AC waveforms. AC servo motors often incorporate advanced control algorithms and feedback systems to achieve accurate position, velocity, and torque control. These motors are commonly used in industrial automation, CNC machines, robotics, and other applications that demand high precision and dynamic performance.
3. Brushed Servo Motors:
Brushed servo motors feature a traditional brushed DC motor design. They consist of a rotor with a commutator and carbon brushes that make physical contact with the commutator. The brushes provide electrical connections, allowing the motor’s magnetic field to interact with the rotor’s windings. Brushed servo motors are known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, they may require more maintenance due to brush wear, and they generally have lower efficiency and shorter lifespan compared to brushless servo motors.
4. Brushless Servo Motors:
Brushless servo motors, also known as brushless DC (BLDC) motors, offer several advantages over brushed motors. They eliminate the need for brushes and commutators, resulting in improved reliability, higher efficiency, and longer lifespan. Brushless servo motors rely on electronic commutation, typically using Hall effect sensors or encoder feedback for accurate rotor position detection. These motors are widely used in robotics, industrial automation, aerospace, and other applications that require high-performance motion control with minimal maintenance.
5. Linear Servo Motors:
Linear servo motors are designed to provide linear motion instead of rotational motion. They consist of a primary part (stator) and a secondary part (slider or forcer) that interact magnetically to generate linear motion. Linear servo motors offer advantages such as high speed, high acceleration, and precise positioning along a linear axis. They find applications in various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, packaging, printing, and machine tools.
6. Micro Servo Motors:
Micro servo motors are small-sized servo motors often used in applications with limited space and low power requirements. They are commonly found in hobbyist projects, model airplanes, remote-controlled vehicles, and small robotic systems. Micro servo motors are lightweight, compact, and offer reasonable precision and control for their size.
These are some of the different types of servo motors available, each catering to specific applications and requirements. The choice of servo motor type depends on factors such as the desired performance, accuracy, power requirements, environmental conditions, and cost considerations. Understanding the differences between servo motor types is essential for selecting the most suitable motor for a particular application.
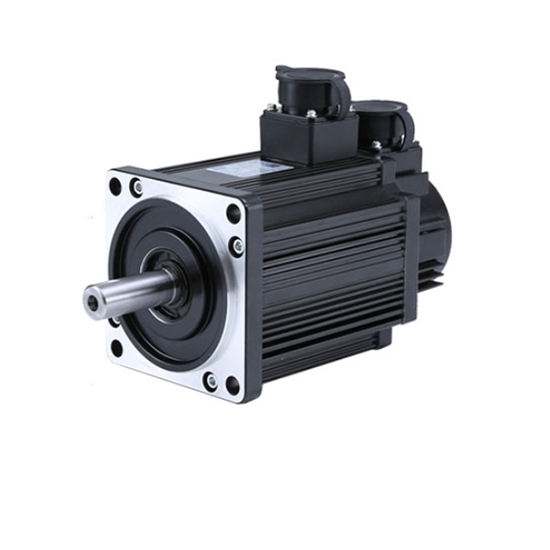

What is a servo motor, and how does it function in automation systems?
A servo motor is a type of motor specifically designed for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. It is widely used in various automation systems where accurate motion control is required. Let’s explore the concept of servo motors and how they function in automation systems:
A servo motor consists of a motor, a position feedback device (such as an encoder or resolver), and a control system. The control system receives input signals, typically in the form of electrical pulses or analog signals, indicating the desired position or speed. Based on these signals and the feedback from the position sensor, the control system adjusts the motor’s operation to achieve the desired motion.
The functioning of a servo motor in an automation system involves the following steps:
- Signal Input: The automation system provides a control signal to the servo motor, indicating the desired position, speed, or other motion parameters. This signal can be generated by a human operator, a computer, a programmable logic controller (PLC), or other control devices.
- Feedback System: The servo motor incorporates a position feedback device, such as an encoder or resolver, which continuously monitors the motor’s actual position. This feedback information is sent back to the control system, allowing it to compare the actual position with the desired position specified by the input signal.
- Control System: The control system, typically housed within the servo motor or an external servo drive, receives the input signal and the feedback from the position sensor. It processes this information and generates the appropriate control signals to the motor.
- Motor Operation: Based on the control signals received from the control system, the servo motor adjusts its operation to achieve the desired motion. The control system varies the motor’s voltage, current, or frequency to control the motor’s speed, torque, or position accurately.
- Closed-Loop Control: Servo motors operate in a closed-loop control system. The feedback information from the position sensor allows the control system to continuously monitor and adjust the motor’s operation to minimize any deviation between the desired position and the actual position. This closed-loop control mechanism provides high accuracy, repeatability, and responsiveness in motion control applications.
One of the key advantages of servo motors in automation systems is their ability to provide precise and dynamic motion control. They can rapidly accelerate, decelerate, and change direction with high accuracy, allowing for intricate and complex movements. Servo motors are widely used in applications such as robotics, CNC machines, printing presses, packaging equipment, and automated manufacturing systems.
In summary, a servo motor is a specialized motor that enables accurate control of position, velocity, and acceleration in automation systems. Through the combination of a control system and a position feedback device, servo motors can precisely adjust their operation to achieve the desired motion. Their closed-loop control mechanism and high responsiveness make them an essential component in various applications requiring precise and dynamic motion control.


editor by CX 2024-05-06
China best OEM RV040 RV050 RV063 Electric Motor with Gear Box Gearbox Nmrv Worm Gear Reducer with high quality
Product Description
Why Choose Us
Product Details
|
Type |
Worm Gear Speed Reducer/ gearbox |
|
Model |
WMRV 25/30/40/50/63/75/90/110/130/150/185 |
|
Ratio |
7.5,10,15,20,25,30,40,50,60,80,100. |
|
Color |
Blue(RAL5571)/Silver grey (K9149) Or On Customer Request |
|
Material |
Housing: Aluminum alloy(size 25~90) / Cast iron(size 110~185) |
|
Worm wheel: Aluminum Bronze or Tin Bronze |
|
| Worm shaft: 20CrMn Ti | |
|
Output Shaft: steel-45# |
|
|
Packing |
Carton, Honey Comb Carton, Wooden Case with wooden pallet |
| Warranty | 1 Year |
| Input Power | 0.09kw,0.18kw,1.1KW,1.5KW,2.2KW,3KW,4KW,5.5KW,7.5KW,11Kw and so on. |
| Usages | Industrial Machine: Food Stuff, Ceramics, CHEMICAL, Packing, Dyeing,Wood working, Glass. |
| IEC Flange | IEC standard flange or on customer request |
| Lubricant | Synthetic oil or worm gear oil |
Company Profile
Exhibition
Customized Service
Certificate&Honor
Customer Comments
FAQ
1. How to choose a gearbox which meets our requirement?
You can refer to our catalogue to choose the gearbox or we can help to choose when you provide
the technical information of required output torque, output speed and motor parameter etc.
2. What information shall we give before placing a purchase order?
a) Type of the gearbox, ratio, input and output type, input flange, mounting position, and motor information etc.
b) Housing color.
c) Purchase quantity.
d) Other special requirements.
3. What industries are your gearboxes being used?
Our gearboxes are widely used in the areas of textile, food processing, beverage, chemical industry,
escalator,automatic storage equipment, metallurgy, tabacco, environmental protection, logistics and etc.
4. Do you sell motors?
We have stable motor suppliers who have been cooperating with us for a long-time. They can provide motors
with high quality.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | 90 Degree |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Gear Shape: | Worm |
| Step: | Double-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 25/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the maintenance requirements for gear motors, and how can longevity be maximized?
Gear motors, like any mechanical system, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance practices help prevent failures, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of gear motors. Here are some maintenance requirements for gear motors and ways to maximize their longevity:
1. Lubrication:
Regular lubrication is essential for gear motors to reduce friction, wear, and heat generation. The gears, bearings, and other moving parts should be properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Lubricants should be selected based on the motor’s specifications and operating conditions. Regular inspection and replenishment of lubricants, as well as periodic oil or grease changes, should be performed to maintain optimal lubrication levels and ensure long-lasting performance.
2. Inspection and Cleaning:
Regular inspection and cleaning of gear motors are crucial for identifying any signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Inspecting the gears, bearings, shafts, and connections can help detect any abnormalities or misalignments. Cleaning the motor’s exterior and ventilation channels to remove dust, debris, or moisture buildup is also important in preventing malfunctions and maintaining proper cooling. Any loose or damaged components should be repaired or replaced promptly.
3. Temperature and Environmental Considerations:
Monitoring and controlling the temperature and environmental conditions surrounding gear motors can significantly impact their longevity. Excessive heat can degrade lubricants, damage insulation, and lead to premature component failure. Ensuring proper ventilation, heat dissipation, and avoiding overloading the motor can help manage temperature effectively. Similarly, protecting gear motors from moisture, dust, chemicals, and other environmental contaminants is vital to prevent corrosion and damage.
4. Load Monitoring and Optimization:
Monitoring and optimizing the load placed on gear motors can contribute to their longevity. Operating gear motors within their specified load and speed ranges helps prevent excessive stress, overheating, and premature wear. Avoiding sudden and frequent acceleration or deceleration, as well as preventing overloading or continuous operation near the motor’s maximum capacity, can extend its lifespan.
5. Alignment and Vibration Analysis:
Proper alignment of gear motor components, such as gears, couplings, and shafts, is crucial for smooth and efficient operation. Misalignment can lead to increased friction, noise, and premature wear. Regularly checking and adjusting alignment, as well as performing vibration analysis, can help identify any misalignment or excessive vibration that may indicate underlying issues. Addressing alignment and vibration problems promptly can prevent further damage and maximize the motor’s longevity.
6. Preventive Maintenance and Regular Inspections:
Implementing a preventive maintenance program is essential for gear motors. This includes establishing a schedule for routine inspections, lubrication, and cleaning, as well as conducting periodic performance tests and measurements. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance tasks, such as belt tension checks, bearing replacements, or gear inspections, can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major failures.
By adhering to these maintenance requirements and best practices, the longevity of gear motors can be maximized. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, load optimization, temperature control, and timely repairs or replacements of worn components contribute to the reliable operation and extended lifespan of gear motors.

How do gear motors compare to other types of motors in terms of power and efficiency?
Gear motors can be compared to other types of motors in terms of power output and efficiency. The choice of motor type depends on the specific application requirements, including the desired power level, efficiency, speed range, torque characteristics, and control capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gear motors compare to other types of motors in terms of power and efficiency:
1. Gear Motors:
Gear motors combine a motor with a gear mechanism to deliver increased torque output and improved control. The gear reduction enables gear motors to provide higher torque while reducing the output speed. This makes gear motors suitable for applications that require high torque, precise positioning, and controlled movements. However, the gear reduction process introduces mechanical losses, which can slightly reduce the overall efficiency of the system compared to direct-drive motors. The efficiency of gear motors can vary depending on factors such as gear quality, lubrication, and maintenance.
2. Direct-Drive Motors:
Direct-drive motors, also known as gearless or integrated motors, do not use a gear mechanism. They provide a direct connection between the motor and the load, eliminating the need for gear reduction. Direct-drive motors offer advantages such as high efficiency, low maintenance, and compact design. Since there are no gears involved, direct-drive motors experience fewer mechanical losses and can achieve higher overall efficiency compared to gear motors. However, direct-drive motors may have limitations in terms of torque output and speed range, and they may require more complex control systems to achieve precise positioning.
3. Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors are a type of gear motor that excels in precise positioning applications. They operate by converting electrical pulses into incremental steps of movement. Stepper motors offer excellent positional accuracy and control. They are capable of precise positioning and can hold a position without power. Stepper motors have relatively high torque at low speeds, making them suitable for applications that require precise control and positioning, such as robotics, 3D printers, and CNC machines. However, stepper motors may have lower overall efficiency compared to direct-drive motors due to the additional power required to overcome the detents between steps.
4. Servo Motors:
Servo motors are another type of gear motor known for their high torque, high speed, and excellent positional accuracy. Servo motors combine a motor, a feedback device (such as an encoder), and a closed-loop control system. They offer precise control over position, speed, and torque. Servo motors are widely used in applications that require accurate and responsive positioning, such as industrial automation, robotics, and camera pan-tilt systems. Servo motors can achieve high efficiency when properly optimized and controlled but may have slightly lower efficiency compared to direct-drive motors due to the additional complexity of the control system.
5. Efficiency Considerations:
When comparing power and efficiency among different motor types, it’s important to consider the specific requirements and operating conditions of the application. Factors such as load characteristics, speed range, duty cycle, and control requirements influence the overall efficiency of the motor system. While direct-drive motors generally offer higher efficiency due to the absence of mechanical losses from gears, gear motors can deliver higher torque output and enhanced control capabilities. The efficiency of gear motors can be optimized through proper gear selection, lubrication, and maintenance practices.
In summary, gear motors offer increased torque and improved control compared to direct-drive motors. However, gear reduction introduces mechanical losses that can slightly impact the overall efficiency of the system. Direct-drive motors, on the other hand, provide high efficiency and compact design but may have limitations in terms of torque and speed range. Stepper motors and servo motors, both types of gear motors, excel in precise positioning applications but may have slightly lower efficiency compared to direct-drive motors. The selection of the most suitable motor type depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing power, efficiency, speed range, and control capabilities.

Are there specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application?
When selecting a gear motor for a specific application, several considerations need to be taken into account. The choice of the right gear motor is crucial to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application:
1. Torque Requirement:
The torque requirement of the application is a critical factor in gear motor selection. Determine the maximum torque that the gear motor needs to deliver to perform the required tasks. Consider both the starting torque (the torque required to initiate motion) and the operating torque (the torque required to sustain motion). Select a gear motor that can provide adequate torque to handle the load requirements of the application. It’s important to account for any potential torque spikes or variations during operation.
2. Speed Requirement:
Consider the desired speed range or specific speed requirements of the application. Determine the rotational speed (in RPM) that the gear motor needs to achieve to meet the application’s performance criteria. Select a gear motor with a suitable gear ratio that can achieve the desired speed at the output shaft. Ensure that the gear motor can maintain the required speed consistently and accurately throughout the operation.
3. Duty Cycle:
Evaluate the duty cycle of the application, which refers to the ratio of operating time to rest or idle time. Consider whether the application requires continuous operation or intermittent operation. Determine the duty cycle’s impact on the gear motor, including factors such as heat generation, cooling requirements, and potential wear and tear. Select a gear motor that is designed to handle the expected duty cycle and ensure long-term reliability and durability.
4. Environmental Factors:
Take into account the environmental conditions in which the gear motor will operate. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, dust, vibrations, and exposure to chemicals or corrosive substances. Choose a gear motor that is specifically designed to withstand and perform optimally under the anticipated environmental conditions. This may involve selecting gear motors with appropriate sealing, protective coatings, or materials that can resist corrosion and withstand harsh environments.
5. Efficiency and Power Requirements:
Consider the desired efficiency and power consumption of the gear motor. Evaluate the power supply available for the application and select a gear motor that operates within the specified voltage and current ranges. Assess the gear motor’s efficiency to ensure that it maximizes power transmission and minimizes wasted energy. Choosing an efficient gear motor can contribute to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
6. Physical Constraints:
Assess the physical constraints of the application, including space limitations, mounting options, and integration requirements. Consider the size, dimensions, and weight of the gear motor to ensure it can be accommodated within the available space. Evaluate the mounting options and compatibility with the application’s mechanical structure. Additionally, consider any specific integration requirements, such as shaft dimensions, connectors, or interfaces that need to align with the application’s design.
7. Noise and Vibration:
Depending on the application, noise and vibration levels may be critical factors. Evaluate the acceptable noise and vibration levels for the application’s environment and operation. Choose a gear motor that is designed to minimize noise and vibration, such as those with helical gears or precision engineering. This is particularly important in applications that require quiet operation or where excessive noise and vibration may cause issues or discomfort.
By considering these specific factors when selecting a gear motor for a particular application, you can ensure that the chosen gear motor meets the performance requirements, operates efficiently, and provides reliable and consistent power transmission. It’s important to consult with gear motor manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable gear motor based on the specific application’s needs.


editor by CX 2024-02-23
China best Three Phase Asynchronous AC Induction Electric Gear Reducer Fan Blower Vacuum Air Compressor Water Pump Universal Industry Machine Motor vacuum pump ac system
Product Description
Product Description
Introduction:
Y2 series three-phase asynchronous motor is Y series motor the upgrading of product, is the totally enclosed, fan-cooled induction motor for general purpose .
It was the newest product in the 90S’ ,its overall level has reached the same products abroad at the beginning of 90S’level. The product apply to economic lake-off fields, such as machine tools, water pump, fan, compressor, also can be applied to transportation, stirring, printing, agricultural machinery, food and other kinds of excluding inflammable, explosive or corrosive gas.
Y2 series three phase asynchronous motor installation size and power grade in conformity with relevant standards of IEC and Germany DIN42673 standard line and Y series motor, its shell protection grade for IP54, cooling method for IC41l, operate continuously (S1). Using F insulation class and grade B assessment according to temperature (except for 315 L2-2, 4355 all specifications F grade the assessment, and ask the assessment load noise index.
Y2 series three-phase asynchronous motor the rated voltage is 380 V. rated frequency is 50 Hz. 3 KW the following connection is Y , other power are delta connection . Motor running the place at no more than 1000 m; Environment air temperature changes with seasons, but no more than 40 °C; Minimum environment air temperature is-15 °C; The wet month average high relative humidity is 90%; At the same time, this month is not higher than the lowest average temperature 25 °C.
Motor Features:
1. Frame size:H56-355;
2. Power:0.12-315Kw;
3. Voltage: 380V;
4. Rated Frequency: 50 Hz / 60 Hz;
5. Poles: 2 / 4 / 6 / 8 / 10
6. Speed: 590 -2980 r/min
7. Ambient Temperature: -15°C-40°C
8. Model of CONEECTION: Y-Connection for 3 KW motor or less while Delta-Connection for 4 KW motor or more;
9. Mounting: B3; B5; B35; B14; B34;
10. Current: 1.5-465 A (AC);
11. Duty: continuous (S1);
12. Insulation Class: B;
13. Protection Class: IP44,IP54,IP55;
14. Frame material: aluminum body(56-132 frame), cast iron(71-355 frame)
15. Terminal box : Top or Side
16. Cooling Method: IC411 Standards;
17. Altitude: No more than 1,000 meters above sea level;
18. Packing: 63-112 frame be packaged by carton&pallets
132-355 frame be packaged by plywood case;
19. Certifications: CE, CCC, ISO9001: 2008
Factory Advantages
1 . 15 years history
2. Competitive Price
3. Guaranteed Quality
4. Fast delivery time, Normal models about 15-20days , another not normal models need about 30days
5. 100% testing after each process and final testing before packing ,all raw material is good quality .100% cooper wire, Cold-rolled silicon steel sheet,good quaility shafts ,bearings,stators ,fan,fan covers.and so on.
6. High efficiency
7. Low noise
8. Long life
9. Power saving
10. Slight vibration
11. It is newly designed in conformity with the relevant rules of IEC standards, Strictly and Perfect Management is guaranteed for Production ;
12. Professional Service
13. Warranty: 12 months from date of delivery
14. Main Market: South America, Middle East, Southest Asia, Europe,Africa and so on
15. We have Certification for CE, CCC, ISO9001,High quality and competitive price !
Installation Instructions
| Y2 Three-phase Asynchronous Electric Motor | |
| 1). Power: | 0.12KW-315KW; |
| 2). Frame: | H56 to 355; |
| 3). Shell: | cast iron body , aluminum body ; |
| 4). Pole: | 2/4/6/8 poles; |
| 5). Mounting arrangement: | B3/B5/B14/B35/B34 or other; |
| 6). Voltage: | 220V, 380V, 400V, 415V, 440V or on request (50Hz or 60Hz); |
| 7). Protection class: | IP54 / IP55 /IP65; |
| 8). Duty/Rating: | S1 (Continuous); |
| 9). Cooling method: | IC411 (SELF-FAN cooling); |
| 10). Insulation class: | F; |
| 11).Standard: | (IEC) EN60034-1 & EN1065714-1. |
Technical Data
| TYPE | OUTPUT | FULL LOAD | Ist/TN | Tst/TN | Tmax/TN | |||||
| HP | KW | Speed (RPM) |
Current (A) |
Efficiency η(%) |
Power Factor (cosΦ) |
|||||
| Synchronous Speed 3000 rpm | ||||||||||
| Y2-631-2 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 2720 | 0.53 | 65 | 0.80 | 5.5 | 2.2 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-632-2 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 2720 | 0.69 | 68 | 0.81 | 5.5 | 2.2 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-711-2 | 0.37 | 0.5 | 2740 | 0.99 | 70 | 0.81 | 6.1 | 2.2 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-712-2 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 2740 | 1.4 | 73 | 0.82 | 6.1 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-801-2 | 0.75 | 1 | 2835 | 1.83 | 77.4 | 0.83 | 6.1 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-802-2 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2835 | 2.58 | 79.6 | 0.84 | 7 | 2.2 | .2.3 | |
| Y2-90S-2 | 1.5 | 2 | 2845 | 3.43 | 81.3 | 0.84 | 7 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-90L-2 | 2.2 | 3 | 2845 | 4.85 | 83.2 | 0.85 | 7 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-100L-2 | 3 | 4 | 2875 | 6.31 | 84.6 | 0.87 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-112M-2 | 4 | 5.5 | 2895 | 8.1 | 85.8 | 0.88 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-132S1-2 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 2905 | 11 | 87 | 0.88 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-132S2-2 | 7.5 | 10 | 2905 | 14.9 | 88.1 | 0.88 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-160M1-2 | 11 | 15 | 2935 | 21.3 | 89.4 | 0.89 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-160M2-2 | 15 | 20 | 2935 | 28.8 | 90.3 | 0.89 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-160L-2 | 18.5 | 25 | 2935 | 34.7 | 90.9 | 0.90 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-180M-2 | 22 | 30 | 2945 | 41 | 91.3 | 0.90 | 7.5 | 2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-200L1-2 | 30 | 40 | 2955 | 55.5 | 92 | 0.90 | 7.5 | 2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-200L2-2 | 37 | 50 | 2955 | 67.9 | 92.5 | 0.90 | 7.5 | 2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-225M-2 | 45 | 60 | 2975 | 82.3 | 92.9 | 0.92 | 7.5 | 2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-250M-2 | 55 | 75 | 2975 | 101 | 93.2 | 0.90 | 7.5 | 2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-280S-2 | 75 | 100 | 2975 | 134 | 93.8 | 0.90 | 7.5 | 2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-315S-2 | 110 | 150 | 2980 | 195 | 94.3 | 0.91 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-315M-2 | 132 | 180 | 2980 | 233 | 94.6 | 0.91 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-315L1-2 | 160 | 200 | 2980 | 279 | 94.8 | 0.92 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-315L2-2 | 200 | 270 | 2980 | 348 | 95 | 0.92 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-355M-2 | 250 | 340 | 2980 | 433 | 95 | 0.92 | 7.1 | 1.6 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-355L-2 | 315 | 430 | 2980 | 544 | 95 | 0.92 | 5.8 | 1.6 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-400M1-2 | 355 | 475 | 2975 | 618 | 95.9 | 0.91 | 5.8 | 1.23 | 2.53 | |
| Y2-400M2-2 | 400 | 535 | 2982 | 689 | 96.0 | 0.92 | 5.74 | 1.31 | 2.43 | |
| Y2-400M3-2 | 450 | 600 | 2982 | 775 | 96.1 | 0.92 | 7.27 | 1.83 | 2.98 | |
| Y2-400L1-2 | 500 | 670 | 2982 | 853 | 96.3 | 0.92 | 6.14 | 1.2 | 2.9 | |
| Y2-400L2-2 | 560 | 750 | 2982 | 952 | 96.3 | 0.92 | 5.46 | 0.98 | 2.57 | |
| Synchronous Speed 1500 rpm | ||||||||||
| Y2-631-4 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 1310 | 0.44 | 57 | 0.72 | 4.4 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-632-4 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 1310 | 1.62 | 60 | 0.73 | 4.4 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-711-4 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 1330 | 0.79 | 65 | 0.75 | 5.2 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-712-4 | 0.37 | 0.5 | 1330 | 1.12 | 67 | 0.74 | 5.2 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-801-4 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 1395 | 1.57 | 71 | 0.75 | 5.2 | 2.4 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-802-4 | 0.75 | 1 | 1395 | 2.03 | 79.6 | 0.76 | 6 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-90S-4 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1405 | 2.89 | 81.4 | 0.77 | 6 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-90L-4 | 1.5 | 2 | 1405 | 3.7 | 82.8 | 0.79 | 6 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-100L1-4 | 2.2 | 3 | 1435 | 5.16 | 84.3 | 0.81 | 7 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-100L2-4 | 3 | 4 | 1435 | 6.78 | 85.5 | 0.82 | 7 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-112M-4 | 4 | 5.5 | 1445 | 8.8 | 86.6 | 0.82 | 7 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-132S-4 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 1445 | 11.7 | 87.7 | 0.83 | 7 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-132M-4 | 7.5 | 10 | 1445 | 15.6 | 88.7 | 0.84 | 7 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-160M-4 | 11 | 15 | 1460 | 22.3 | 89.8 | 0.84 | 7 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-160L-4 | 15 | 20 | 1460 | 30.1 | 90.6 | 0.85 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-180M-4 | 18.5 | 25 | 1470 | 36.5 | 91.2 | 0.86 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-180L-4 | 22 | 30 | 1470 | 43.2 | 91.6 | 0.86 | 7.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-200L-4 | 30 | 40 | 1470 | 57.6 | 92.3 | 0.86 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-225S-4 | 37 | 50 | 1485 | 69.9 | 92.7 | 0.87 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-225M-4 | 45 | 60 | 1485 | 84.7 | 93.1 | 0.87 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-250M-4 | 55 | 75 | 1485 | 103 | 93.5 | 0.87 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-280S-4 | 75 | 100 | 1485 | 140 | 94 | 0.87 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-280M-4 | 90 | 125 | 1490 | 167 | 94.2 | 0.87 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| Y2-315S-4 | 110 | 150 | 1490 | 201 | 94.5 | 0.88 | 6.9 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-315M-4 | 132 | 180 | 1490 | 240 | 94.7 | 0.88 | 6.9 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-315L1-4 | 160 | 200 | 1490 | 287 | 94.9 | 0.89 | 6.9 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-315L2-4 | 200 | 270 | 1490 | 359 | 94.1 | 0.89 | 6.9 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-355M-4 | 250 | 340 | 1485 | 443 | 95.1 | 0.90 | 6.9 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-355L-4 | 315 | 430 | 1485 | 556 | 95.1 | 0.90 | 6.9 | 2.1 | 2.2 | |
| Y2-400M1-4 | 355 | 475 | 1490 | 641 | 95.5 | 0.88 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 1.93 | |
| Y2-400M2-4 | 400 | 535 | 1490 | 723 | 95.5 | 0.88 | 6.5 | 2.75 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400M3-4 | 450 | 600 | 1490 | 804 | 95.5 | 0.89 | 6.5 | 2.81 | 2.03 | |
| Y2-400L1-4 | 500 | 670 | 1490 | 893 | 95.6 | 0.89 | 6.61 | 2.52 | 1.83 | |
| Y2-400L2-4 | 560 | 750 | 1490 | 971 | 96.0 | 0.89 | 6.6 | 2.67 | 2.02 | |
| Synchronous Speed 1000 rpm | ||||||||||
| Y2-711-6 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 850 | 0.74 | 56 | 0.66 | 4 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-712-6 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 850 | 0.95 | 59 | 0.68 | 4 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-801-6 | 0.37 | 0.5 | 890 | 1.3 | 62 | 0.70 | 4.7 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-802-6 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 890 | 1.79 | 65 | 0.72 | 4.7 | 1.9 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-90S-6 | 0.7 | 1 | 915 | 2.29 | 75.9 | 0.72 | 5.5 | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-90L-6 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 915 | 3.18 | 78.1 | 0.73 | 5.5 | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-100L-6 | 1.5 | 2 | 945 | 3.94 | 79.8 | 0.75 | 5.5 | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-112M-6 | 2.2 | 3 | 945 | 5.6 | 81.8 | 0.76 | 6.5 | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-132S-6 | 3 | 4 | 965 | 7.4 | 83.3 | 0.76 | 6.5 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-132M1-6 | 4 | 5.5 | 965 | 9.8 | 84.6 | 0.76 | 6.5 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-132M2-6 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 965 | 12.9 | 86 | 0.77 | 6.5 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-160M-6 | 7.5 | 10 | 975 | 17 | 87.2 | 0.78 | 6.5 | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-160L-6 | 11 | 15 | 975 | 24.2 | 88.7 | 0.81 | 7 | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-180L-6 | 15 | 20 | 975 | 31.6 | 89.7 | 0.81 | 7 | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-200L1-6 | 18.5 | 25 | 975 | 38.6 | 90.4 | 0.83 | 7 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-200L2-6 | 22 | 30 | 975 | 44.7 | 90.9 | 0.84 | 7 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-225M-6 | 30 | 40 | 980 | 59.3 | 91.7 | 0.86 | 7 | 2 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-250M-6 | 37 | 50 | 980 | 71 | 92.2 | 0.86 | 7 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| Y2-280S-6 | 45 | 60 | 980 | 86 | 92.7 | 0.86 | 7 | 2.1 | 2 | |
| Y2-280M-6 | 55 | 75 | 980 | 105 | 93.1 | 0.86 | 7 | 2.1 | 2 | |
| Y2-315S-6 | 75 | 100 | 980 | 141 | 93.7 | 0.86 | 7 | 2 | 2 | |
| Y2-315M-6 | 90 | 125 | 980 | 169 | 94 | 0.86 | 7 | 2 | 2 | |
| Y2-315L1-6 | 110 | 150 | 980 | 206 | 94.3 | 0.86 | 6.7 | 2 | 2 | |
| Y2-315L2-6 | 132 | 180 | 980 | 244 | 94.6 | 0.87 | 6.7 | 2 | 2 | |
| Y2-355M1-6 | 160 | 200 | 985 | 292 | 94.8 | 0.88 | 6.7 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-355M2-6 | 200 | 270 | 985 | 365 | 95 | 0.88 | 6.7 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-355L-6 | 250 | 340 | 985 | 455 | 95 | 0.88 | 6.7 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-400M1-6 | 280 | 380 | 990 | 510 | 95.8 | 0.87 | 5.9 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400M2-6 | 315 | 430 | 990 | 574 | 95.8 | 0.87 | 5.9 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400M3-6 | 355 | 475 | 990 | 638 | 95.8 | 0.87 | 5.9 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400L1-6 | 400 | 535 | 990 | 719 | 96.0 | 0.88 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400L2-6 | 450 | 600 | 990 | 796 | 96.5 | 0.89 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Synchronous Speed 750 rpm | ||||||||||
| Y2-801-8 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 630 | 0.88 | 51 | 0.61 | 3.3 | 1.8 | 1.9 | |
| Y2-802-8 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 640 | 1.15 | 54 | 0.61 | 3.3 | 1.8 | 1.9 | |
| Y2-90S-8 | 0.37 | 0.5 | 660 | 1.49 | 62 | 0.61 | 4 | 1.8 | 1.9 | |
| Y2-90L-8 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 660 | 2.18 | 63 | 0.61 | 4 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-100L1-8 | 0.75 | 1 | 680 | 2.39 | 71 | 0.67 | 4 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-100L2-8 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 680 | 3.32 | 73 | 0.69 | 5 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-112M-8 | 1.5 | 2 | 690 | 4.5 | 75 | 0.69 | 5 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-132S-8 | 2.2 | 3 | 690 | 6 | 78 | 0.71 | 6 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-132M-8 | 3 | 4 | 710 | 7.9 | 79 | 0.73 | 6 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-160M1-8 | 4 | 5 | 710 | 10.3 | 81 | 0.73 | 6 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-160M2-8 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 720 | 13.6 | 83 | 0.74 | 6 | 2 | 2 | |
| Y2-160L-8 | 7.5 | 10 | 720 | 17.8 | 85.5 | 0.75 | 6 | 2 | 2 | |
| Y2-180L-8 | 11 | 15 | 730 | 25.1 | 87.5 | 0.76 | 6.6 | 2 | 2 | |
| Y2-200L-8 | 15 | 20 | 730 | 34.1 | 88 | 0.76 | 6.6 | 2 | 2 | |
| Y2-225S-8 | 18.5 | 25 | 730 | 40.6 | 90 | 0.76 | 6.6 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-225M-8 | 22 | 30 | 740 | 47.4 | 90.5 | 0.78 | 6.6 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-250M-8 | 30 | 40 | 740 | 64 | 91 | 0.79 | 6.6 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-280S-8 | 37 | 50 | 740 | 78 | 91.5 | 0.79 | 6.6 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-280M-8 | 45 | 60 | 740 | 94 | 92 | 0.79 | 6.6 | 1.9 | 2 | |
| Y2-315S-8 | 55 | 75 | 740 | 111 | 92.8 | 0.81 | 6.6 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-315M-8 | 75 | 100 | 740 | 151 | 93 | 0.81 | 6.6 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-315L1-8 | 90 | 125 | 740 | 178 | 93.8 | 0.82 | 6.6 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-315L2-8 | 110 | 150 | 740 | 217 | 94 | 0.82 | 7.2 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-355M1-8 | 132 | 180 | 740 | 261 | 93.7 | 0.82 | 7.2 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-355M2-8 | 160 | 200 | 740 | 315 | 94.2 | 0.82 | 7.2 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-355L-8 | 200 | 270 | 740 | 388 | 94.5 | 0.83 | 7.2 | 1.8 | 2 | |
| Y2-400M1-8 | 250 | 340 | 745 | 494 | 95.0 | 0.81 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400M2-8 | 280 | 380 | 745 | 552 | 95.0 | 0.82 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400L1-8 | 315 | 430 | 745 | 592 | 95.0 | 0.85 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400L2-8 | 355 | 475 | 745 | 692 | 95.0 | 0.85 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400L3-8 | 400 | 535 | 745 | 780 | 95.0 | 0.85 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 1.8 | |
| Synchronous Speed 600 rpm | ||||||||||
| Y2-315S-10 | 45 | 60 | 590 | 100 | 91.5 | 0.75 | 6.2 | 1.5 | 2 | |
| Y2-315M-10 | 55 | 75 | 590 | 121 | 92 | 0.75 | 6.2 | 1.5 | 2 | |
| Y2-315L1-10 | 75 | 100 | 590 | 162 | 92.5 | 0.76 | 6.2 | 1.2 | 2 | |
| Y2-315L2-10 | 90 | 125 | 590 | 191 | 93 | 0.77 | 6.2 | 1.5 | 2 | |
| Y2-355M1-10 | 110 | 150 | 590 | 230 | 93.2 | 0.78 | 6 | 1.3 | 2 | |
| Y2-355M2-10 | 132 | 180 | 590 | 275 | 93.5 | 0.78 | 6 | 1.3 | 2 | |
| Y2-355L-10 | 160 | 200 | 590 | 334 | 93.5 | 0.78 | 6 | 1.3 | 2 | |
| Y2-400M1-10 | 200 | 270 | 595 | 404 | 95.0 | 0.80 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400M2-10 | 250 | 340 | 595 | 495 | 95.0 | 0.81 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400L1-10 | 280 | 380 | 595 | 554 | 95.0 | 0.82 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 1.8 | |
| Y2-400L2-10 | 315 | 430 | 595 | 630 | 95.0 | 0.82 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 1.8 | |
Detailed Photos
Our OEM Motors, Diesel generator sets ,Alternators are talior made to fit the OEM customer’s application. Our based Engineering Design team work with you to ensure the motor meets your individual needs.
2 ,4,6 ,8 and 10 pole operation. with CE Approvals available
All Motors, Diesel generator sets ,Alternators may be designed for optional voltages and frequencies.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Variable Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Three-Phase |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Are there innovations or emerging technologies in the field of gear motor design?
Yes, there are several innovations and emerging technologies in the field of gear motor design. These advancements aim to improve the performance, efficiency, compactness, and reliability of gear motors. Here are some notable innovations and emerging technologies in gear motor design:
1. Miniaturization and Compact Design:
Advancements in manufacturing techniques and materials have enabled the miniaturization of gear motors without compromising their performance. Gear motors with compact designs are highly sought after in applications where space is limited, such as robotics, medical devices, and consumer electronics. Innovative approaches like micro-gear motors and integrated motor-gear units are being developed to achieve smaller form factors while maintaining high torque and efficiency.
2. High-Efficiency Gearing:
New gear designs focus on improving efficiency by reducing friction and mechanical losses. Advanced gear manufacturing techniques, such as precision machining and 3D printing, allow for the creation of intricate gear tooth profiles that optimize power transmission and minimize losses. Additionally, the use of high-performance materials, coatings, and lubricants helps reduce friction and wear, improving overall gear motor efficiency.
3. Magnetic Gearing:
Magnetic gearing is an emerging technology that replaces traditional mechanical gears with magnetic fields to transmit torque. It utilizes the interaction of permanent magnets to transfer power, eliminating the need for physical gear meshing. Magnetic gearing offers advantages such as high efficiency, low noise, compactness, and maintenance-free operation. While still being developed and refined, magnetic gearing holds promise for various applications, including gear motors.
4. Integrated Electronics and Controls:
Gear motor designs are incorporating integrated electronics and controls to enhance performance and functionality. Integrated motor drives and controllers simplify system integration, reduce wiring complexity, and allow for advanced control features. These integrated solutions offer precise speed and torque control, intelligent feedback mechanisms, and connectivity options for seamless integration into automation systems and IoT (Internet of Things) platforms.
5. Smart and Condition Monitoring Capabilities:
New gear motor designs incorporate smart features and condition monitoring capabilities to enable predictive maintenance and optimize performance. Integrated sensors and monitoring systems can detect abnormal operating conditions, track performance parameters, and provide real-time feedback for proactive maintenance and troubleshooting. This helps prevent unexpected failures, extend the lifespan of gear motors, and improve overall system reliability.
6. Energy-Efficient Motor Technologies:
Gear motor design is influenced by advancements in energy-efficient motor technologies. Brushless DC (BLDC) motors and synchronous reluctance motors (SynRM) are gaining popularity due to their higher efficiency, better power density, and improved controllability compared to traditional brushed DC and induction motors. These motor technologies, when combined with optimized gear designs, contribute to overall system energy savings and performance improvements.
These are just a few examples of the innovations and emerging technologies in gear motor design. The field is continuously evolving, driven by the need for more efficient, compact, and reliable motion control solutions in various industries. Gear motor manufacturers and researchers are actively exploring new materials, manufacturing techniques, control strategies, and system integration approaches to meet the evolving demands of modern applications.

Can gear motors be used for precise positioning, and if so, what features enable this?
Yes, gear motors can be used for precise positioning in various applications. The combination of gear mechanisms and motor control features enables gear motors to achieve accurate and repeatable positioning. Here’s a detailed explanation of the features that enable gear motors to be used for precise positioning:
1. Gear Reduction:
One of the key features of gear motors is their ability to provide gear reduction. Gear reduction refers to the process of reducing the output speed of the motor while increasing the torque. By using the appropriate gear ratio, gear motors can achieve finer control over the rotational movement, allowing for more precise positioning. The gear reduction mechanism enables the motor to rotate at a slower speed while maintaining higher torque, resulting in improved accuracy and control.
2. High Resolution Encoders:
Many gear motors are equipped with high-resolution encoders. An encoder is a device that measures the position and speed of the motor shaft. High-resolution encoders provide precise feedback on the motor’s rotational position, allowing for accurate position control. The encoder signals are used in conjunction with motor control algorithms to ensure precise positioning by monitoring and adjusting the motor’s movement in real-time. The use of high-resolution encoders greatly enhances the gear motor’s ability to achieve precise and repeatable positioning.
3. Closed-Loop Control:
Gear motors with closed-loop control systems offer enhanced positioning capabilities. Closed-loop control involves continuously comparing the actual motor position (as measured by the encoder) with the desired position and making adjustments to minimize any position error. The closed-loop control system uses feedback from the encoder to adjust the motor’s speed, direction, and torque, ensuring accurate positioning even in the presence of external disturbances or variations in the load. Closed-loop control enables gear motors to actively correct for position errors and maintain precise positioning over time.
4. Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors are a type of gear motor that provides excellent precision and control for positioning applications. Stepper motors operate by converting electrical pulses into incremental steps of movement. Each step corresponds to a specific angular displacement, allowing precise positioning control. Stepper motors offer high step resolution, allowing for fine position adjustments. They are commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, such as robotics, 3D printers, and CNC machines.
5. Servo Motors:
Servo motors are another type of gear motor that excels in precise positioning tasks. Servo motors combine a motor, a feedback device (such as an encoder), and a closed-loop control system. They offer high torque, high speed, and excellent positional accuracy. Servo motors are capable of dynamically adjusting their speed and torque to maintain the desired position accurately. They are widely used in applications that require precise and responsive positioning, such as industrial automation, robotics, and camera pan-tilt systems.
6. Motion Control Algorithms:
Advanced motion control algorithms play a crucial role in enabling gear motors to achieve precise positioning. These algorithms, implemented in motor control systems or dedicated motion controllers, optimize the motor’s behavior to ensure accurate positioning. They take into account factors such as acceleration, deceleration, velocity profiling, and jerk control to achieve smooth and precise movements. Motion control algorithms enhance the gear motor’s ability to start, stop, and position accurately, reducing position errors and overshoot.
By leveraging gear reduction, high-resolution encoders, closed-loop control, stepper motors, servo motors, and motion control algorithms, gear motors can be effectively used for precise positioning in various applications. These features enable gear motors to achieve accurate and repeatable positioning, making them suitable for tasks that require precise control and reliable positioning performance.

How does the gearing mechanism in a gear motor contribute to torque and speed control?
The gearing mechanism in a gear motor plays a crucial role in controlling torque and speed. By utilizing different gear ratios and configurations, the gearing mechanism allows for precise manipulation of these parameters. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the gearing mechanism contributes to torque and speed control in a gear motor:
The gearing mechanism consists of multiple gears with varying sizes, tooth configurations, and arrangements. Each gear in the system engages with another gear, creating a mechanical connection. When the motor rotates, it drives the rotation of the first gear, which then transfers the motion to subsequent gears, ultimately resulting in the output shaft’s rotation.
Torque Control:
The gearing mechanism in a gear motor enables torque control through the principle of mechanical advantage. The gear system utilizes gears with different numbers of teeth, known as gear ratio, to adjust the torque output. When a smaller gear (pinion) engages with a larger gear (gear), the pinion rotates faster than the gear but exerts more force or torque. This results in torque amplification, allowing the gear motor to deliver higher torque at the output shaft while reducing the rotational speed. Conversely, if a larger gear engages with a smaller gear, torque reduction occurs, resulting in higher rotational speed at the output shaft.
By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the gearing mechanism effectively adjusts the torque output of the gear motor to match the requirements of the application. This torque control capability is essential in applications that demand high torque for heavy lifting or overcoming resistance, as well as applications that require lower torque but higher rotational speed.
Speed Control:
The gearing mechanism also contributes to speed control in a gear motor. The gear ratio determines the relationship between the rotational speed of the input shaft (driven by the motor) and the output shaft. When a gear motor has a higher gear ratio (more teeth on the driven gear compared to the driving gear), it reduces the output speed while increasing the torque. Conversely, a lower gear ratio increases the output speed while reducing the torque.
By choosing the appropriate gear ratio, the gearing mechanism allows for precise speed control in a gear motor. This is particularly useful in applications that require specific speed ranges or variations, such as conveyor systems, robotic movements, or machinery that needs to operate at different speeds for different tasks. The speed control capability of the gearing mechanism enables the gear motor to match the desired speed requirements of the application accurately.
In summary, the gearing mechanism in a gear motor contributes to torque and speed control by utilizing different gear ratios and configurations. It enables torque amplification or reduction, depending on the gear arrangement, allowing the gear motor to deliver the required torque output. Additionally, the gear ratio also determines the relationship between the rotational speed of the input and output shafts, providing precise speed control. These torque and speed control capabilities make gear motors versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications in various industries.


editor by CX 2024-02-11
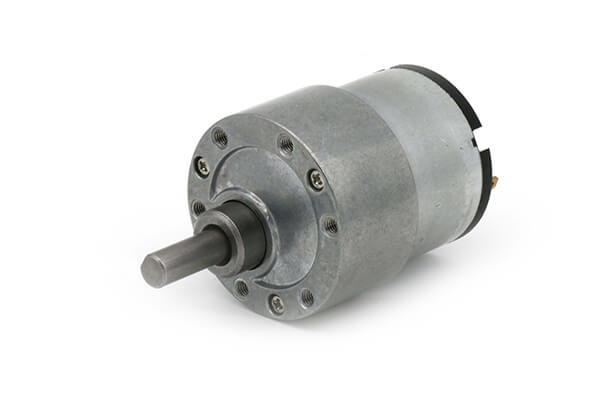
China Custom 12V DC Gear Motor with Reducer 32mm Planetary DC Motor vacuum pump electric
Product Description
Product Pictures
Product Parameter
Brush Motor Technical Data:
|
Model |
Voltage |
Power |
No-Load Current |
No-Load Speed |
Rated Current |
Rated Speed |
Rated Torque |
|
Z32DPN2410-40S |
24V |
10W |
0.40A |
5000rpm |
0.7A |
4000rpm |
0.571N.m |
|
Z32DPN2415-50S |
24V |
15W |
0.50A |
6000rpm |
1.1A |
5000rpm |
0.571N.m |
Brush DC Planetary Gear Motor Technical Data-62DPN2490-30S:
|
Ratio |
3.7 |
4.29 |
5.18 |
6.75 |
14 |
19 |
25 |
29 |
|
Out-put Speed(rpm) |
1081 |
932 |
772 |
592 |
285 |
210 |
160 |
137 |
|
Allowable Torque(N.m) |
0.08 |
0.092 |
0.111 |
0.145 |
0.27 |
0.367 |
0.483 |
0.561 |
|
Reduction Stage |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ratio |
35 |
46 |
51 |
68 |
79 |
93 |
100 |
115 |
|
Out-put Speed(rpm) |
114 |
87 |
78 |
59 |
50 |
43 |
40 |
35 |
|
Allowable Torque(N.m) |
0.6777 |
0.89 |
0.889 |
1.185 |
1.3777 |
1.621 |
1.743 |
2.004 |
|
Reduction Stage |
2 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ratio |
130 |
150 |
169 |
195 |
236 |
308 |
|
|
|
Out-put Speed(rpm) |
31 |
26 |
23 |
20 |
17 |
13 |
|
|
|
Allowable Torque(N.m) |
2.266 |
2.614 |
2.945 |
3.400 |
4.000 |
4.000 |
|
|
|
Reduction Stage |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|
|
Product Advantages
Planetary gear reducer is a new generation of practical products independently developed by our company ,which has the following main features:
*Low noise *Hight torque
*Low Backlash *High stability
*High efficiency *High input speed
Product detailsProduct Application
Related Products:
Our products have the features of small size,light weight,high bearing capacity ,long service life,smooth
operation ,low noise,large output torque,high speed ratio,high efficiency and safe performance.
It has the characteristics of power split and multi-tooth meshing.
We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc Gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors,
Brushless DC Motors, Stepper motors, Ac Motors and High Precision Planetary Gear Box etc.
You can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification.
Company profile
LunYee Culture:
L-Loyalty to Customers
U-Unity of working together
N-New things introduced by us in our industry
Y-Yield returns and enjoy together
E- Easy to buy
E- Easy to use
A satisfying one-stop service comes from our continuous innovation team and our rigorously-inspected sub-contracters!
Our products are widely applied to machine tools, industrial robot,textile machine,packing machine,food machine, medical appliance,CNC system and air condition and so on!
FAQ:
Q1. Can I have a sample order?
A: Yes, we can sell a sample, sit is pleased to receive a sample order to test and check the quality of products.
Q2. How long is the warranty?
A: The products come with a one-year warranty.
Q3. Can our logo be printed on this product?
A: Yes, please inform us formally before production and confirm the design firstly based on our sample.
| Application: | Universal |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | High Speed |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brush |
| Brand: | Lunyee |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Are there innovations or emerging technologies in the field of gear motor design?
Yes, there are several innovations and emerging technologies in the field of gear motor design. These advancements aim to improve the performance, efficiency, compactness, and reliability of gear motors. Here are some notable innovations and emerging technologies in gear motor design:
1. Miniaturization and Compact Design:
Advancements in manufacturing techniques and materials have enabled the miniaturization of gear motors without compromising their performance. Gear motors with compact designs are highly sought after in applications where space is limited, such as robotics, medical devices, and consumer electronics. Innovative approaches like micro-gear motors and integrated motor-gear units are being developed to achieve smaller form factors while maintaining high torque and efficiency.
2. High-Efficiency Gearing:
New gear designs focus on improving efficiency by reducing friction and mechanical losses. Advanced gear manufacturing techniques, such as precision machining and 3D printing, allow for the creation of intricate gear tooth profiles that optimize power transmission and minimize losses. Additionally, the use of high-performance materials, coatings, and lubricants helps reduce friction and wear, improving overall gear motor efficiency.
3. Magnetic Gearing:
Magnetic gearing is an emerging technology that replaces traditional mechanical gears with magnetic fields to transmit torque. It utilizes the interaction of permanent magnets to transfer power, eliminating the need for physical gear meshing. Magnetic gearing offers advantages such as high efficiency, low noise, compactness, and maintenance-free operation. While still being developed and refined, magnetic gearing holds promise for various applications, including gear motors.
4. Integrated Electronics and Controls:
Gear motor designs are incorporating integrated electronics and controls to enhance performance and functionality. Integrated motor drives and controllers simplify system integration, reduce wiring complexity, and allow for advanced control features. These integrated solutions offer precise speed and torque control, intelligent feedback mechanisms, and connectivity options for seamless integration into automation systems and IoT (Internet of Things) platforms.
5. Smart and Condition Monitoring Capabilities:
New gear motor designs incorporate smart features and condition monitoring capabilities to enable predictive maintenance and optimize performance. Integrated sensors and monitoring systems can detect abnormal operating conditions, track performance parameters, and provide real-time feedback for proactive maintenance and troubleshooting. This helps prevent unexpected failures, extend the lifespan of gear motors, and improve overall system reliability.
6. Energy-Efficient Motor Technologies:
Gear motor design is influenced by advancements in energy-efficient motor technologies. Brushless DC (BLDC) motors and synchronous reluctance motors (SynRM) are gaining popularity due to their higher efficiency, better power density, and improved controllability compared to traditional brushed DC and induction motors. These motor technologies, when combined with optimized gear designs, contribute to overall system energy savings and performance improvements.
These are just a few examples of the innovations and emerging technologies in gear motor design. The field is continuously evolving, driven by the need for more efficient, compact, and reliable motion control solutions in various industries. Gear motor manufacturers and researchers are actively exploring new materials, manufacturing techniques, control strategies, and system integration approaches to meet the evolving demands of modern applications.

How do gear motors compare to other types of motors in terms of power and efficiency?
Gear motors can be compared to other types of motors in terms of power output and efficiency. The choice of motor type depends on the specific application requirements, including the desired power level, efficiency, speed range, torque characteristics, and control capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gear motors compare to other types of motors in terms of power and efficiency:
1. Gear Motors:
Gear motors combine a motor with a gear mechanism to deliver increased torque output and improved control. The gear reduction enables gear motors to provide higher torque while reducing the output speed. This makes gear motors suitable for applications that require high torque, precise positioning, and controlled movements. However, the gear reduction process introduces mechanical losses, which can slightly reduce the overall efficiency of the system compared to direct-drive motors. The efficiency of gear motors can vary depending on factors such as gear quality, lubrication, and maintenance.
2. Direct-Drive Motors:
Direct-drive motors, also known as gearless or integrated motors, do not use a gear mechanism. They provide a direct connection between the motor and the load, eliminating the need for gear reduction. Direct-drive motors offer advantages such as high efficiency, low maintenance, and compact design. Since there are no gears involved, direct-drive motors experience fewer mechanical losses and can achieve higher overall efficiency compared to gear motors. However, direct-drive motors may have limitations in terms of torque output and speed range, and they may require more complex control systems to achieve precise positioning.
3. Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors are a type of gear motor that excels in precise positioning applications. They operate by converting electrical pulses into incremental steps of movement. Stepper motors offer excellent positional accuracy and control. They are capable of precise positioning and can hold a position without power. Stepper motors have relatively high torque at low speeds, making them suitable for applications that require precise control and positioning, such as robotics, 3D printers, and CNC machines. However, stepper motors may have lower overall efficiency compared to direct-drive motors due to the additional power required to overcome the detents between steps.
4. Servo Motors:
Servo motors are another type of gear motor known for their high torque, high speed, and excellent positional accuracy. Servo motors combine a motor, a feedback device (such as an encoder), and a closed-loop control system. They offer precise control over position, speed, and torque. Servo motors are widely used in applications that require accurate and responsive positioning, such as industrial automation, robotics, and camera pan-tilt systems. Servo motors can achieve high efficiency when properly optimized and controlled but may have slightly lower efficiency compared to direct-drive motors due to the additional complexity of the control system.
5. Efficiency Considerations:
When comparing power and efficiency among different motor types, it’s important to consider the specific requirements and operating conditions of the application. Factors such as load characteristics, speed range, duty cycle, and control requirements influence the overall efficiency of the motor system. While direct-drive motors generally offer higher efficiency due to the absence of mechanical losses from gears, gear motors can deliver higher torque output and enhanced control capabilities. The efficiency of gear motors can be optimized through proper gear selection, lubrication, and maintenance practices.
In summary, gear motors offer increased torque and improved control compared to direct-drive motors. However, gear reduction introduces mechanical losses that can slightly impact the overall efficiency of the system. Direct-drive motors, on the other hand, provide high efficiency and compact design but may have limitations in terms of torque and speed range. Stepper motors and servo motors, both types of gear motors, excel in precise positioning applications but may have slightly lower efficiency compared to direct-drive motors. The selection of the most suitable motor type depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing power, efficiency, speed range, and control capabilities.

Are there specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application?
When selecting a gear motor for a specific application, several considerations need to be taken into account. The choice of the right gear motor is crucial to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application:
1. Torque Requirement:
The torque requirement of the application is a critical factor in gear motor selection. Determine the maximum torque that the gear motor needs to deliver to perform the required tasks. Consider both the starting torque (the torque required to initiate motion) and the operating torque (the torque required to sustain motion). Select a gear motor that can provide adequate torque to handle the load requirements of the application. It’s important to account for any potential torque spikes or variations during operation.
2. Speed Requirement:
Consider the desired speed range or specific speed requirements of the application. Determine the rotational speed (in RPM) that the gear motor needs to achieve to meet the application’s performance criteria. Select a gear motor with a suitable gear ratio that can achieve the desired speed at the output shaft. Ensure that the gear motor can maintain the required speed consistently and accurately throughout the operation.
3. Duty Cycle:
Evaluate the duty cycle of the application, which refers to the ratio of operating time to rest or idle time. Consider whether the application requires continuous operation or intermittent operation. Determine the duty cycle’s impact on the gear motor, including factors such as heat generation, cooling requirements, and potential wear and tear. Select a gear motor that is designed to handle the expected duty cycle and ensure long-term reliability and durability.
4. Environmental Factors:
Take into account the environmental conditions in which the gear motor will operate. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, dust, vibrations, and exposure to chemicals or corrosive substances. Choose a gear motor that is specifically designed to withstand and perform optimally under the anticipated environmental conditions. This may involve selecting gear motors with appropriate sealing, protective coatings, or materials that can resist corrosion and withstand harsh environments.
5. Efficiency and Power Requirements:
Consider the desired efficiency and power consumption of the gear motor. Evaluate the power supply available for the application and select a gear motor that operates within the specified voltage and current ranges. Assess the gear motor’s efficiency to ensure that it maximizes power transmission and minimizes wasted energy. Choosing an efficient gear motor can contribute to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
6. Physical Constraints:
Assess the physical constraints of the application, including space limitations, mounting options, and integration requirements. Consider the size, dimensions, and weight of the gear motor to ensure it can be accommodated within the available space. Evaluate the mounting options and compatibility with the application’s mechanical structure. Additionally, consider any specific integration requirements, such as shaft dimensions, connectors, or interfaces that need to align with the application’s design.
7. Noise and Vibration:
Depending on the application, noise and vibration levels may be critical factors. Evaluate the acceptable noise and vibration levels for the application’s environment and operation. Choose a gear motor that is designed to minimize noise and vibration, such as those with helical gears or precision engineering. This is particularly important in applications that require quiet operation or where excessive noise and vibration may cause issues or discomfort.
By considering these specific factors when selecting a gear motor for a particular application, you can ensure that the chosen gear motor meets the performance requirements, operates efficiently, and provides reliable and consistent power transmission. It’s important to consult with gear motor manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable gear motor based on the specific application’s needs.


editor by CX 2023-11-29
China factory NEMA 17 24V 42mm Electric Brushless DC Precision Planetary Gear Motor Gearbox Reducer BLDC Motor motor armature
Product Description
General Specification:
Step Angle Accuracy: ±5%
Resistance Accuracy: ±10%
Inductance Accuracy: ±20%
Temperature Rise: 80°C Max
Ambient Temperature: -15°C~+50°C
Insulation Resistance: 100MΩ Min., 500VDC
Dielectric Strength: 500VAC for 1 minute
Shaft Radial Play: 0.02Max (450g-load)
Shaft Axial Play: 0.08Max (450g-load)
Specification:
| Model | |||||
| Specification | Unit | JK42BLS01 | JK42BLS02 | JK42BLS03 | JK42BLS04 |
| Number Of Phase | Phase | 3 | |||
| Number Of Poles | Poles | 8 | |||
| Rated Voltage | VDC | 24 | |||
| Rated Speed | Rpm | 4000 | |||
| Rated Torque | N.m | 0.0625 | 0.125 | 0.185 | 0.25 |
| Rated Current | Amps | 1.8 | 3.3 | 4.8 | 6.3 |
| Rated Power | W | 26 | 52.5 | 77.5 | 105 |
| Peak Torque | N.m | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.56 | 0.75 |
| Peak Current | Amps | 5.4 | 10.6 | 15.5 | 20 |
| Back E.M.F | V/Krpm | 4.1 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.3 |
| Torque Constant | N.m/A | 0.039 | 0.04 | 0.041 | 0.041 |
| Rotor Inertia | g.cm² | 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 |
| Body Length | mm | 41 | 61 | 81 | 100 |
| Weight | Kg | 0.3 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.8 |
Dimensions:
(Unit=mm)
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | High Speed |
| Function: | Driving |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brushless |
| Certification: | ISO9001, CCC, CE, RoHS, SGS |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What Is a Gear Motor?
A gear motor is an electric motor coupled with a gear train. It uses either DC or AC power to achieve its purpose. The primary benefit of a gear reducer is its ability to multiply torque while maintaining a compact size. The trade-off of this additional torque comes in the form of a reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, proper gear technology and ratios provide optimum output and speed profiles. This type of motor unlocks the full potential of OEM equipment.
Inertial load
Inertial load on a gear motor is the amount of force a rotating device produces due to its inverse square relationship with its inertia. The greater the inertia, the less torque can be produced by the gear motor. However, if the inertia is too high, it can cause problems with positioning, settling time, and controlling torque and velocity. Gear ratios should be selected for optimal power transfer.
The duration of acceleration and braking time of a gear motor depends on the type of driven load. An inertia load requires longer acceleration time whereas a friction load requires breakaway torque to start the load and maintain it at its desired speed. Too short a time period can cause excessive gear loading and may result in damaged gears. A safe approach is to disconnect the load when power is disconnected to prevent inertia from driving back through the output shaft.
Inertia is a fundamental concept in the design of motors and drive systems. The ratio of mass and inertia of a load to a motor determines how well the motor can control its speed during acceleration or deceleration. The mass moment of inertia, also called rotational inertia, is dependent on the mass, geometry, and center of mass of an object.
Applications
There are many applications of gear motors. They provide a powerful yet efficient means of speed and torque control. They can be either AC or DC, and the two most common motor types are the three-phase asynchronous and the permanent magnet synchronous servomotor. The type of motor used for a given application will determine its cost, reliability, and complexity. Gear motors are typically used in applications where high torque is required and space or power constraints are significant.
There are two types of gear motors. Depending on the ratio, each gear has an output shaft and an input shaft. Gear motors use hydraulic pressure to produce torque. The pressure builds on one side of the motor until it generates enough torque to power a rotating load. This type of motors is not recommended for applications where load reversals occur, as the holding torque will diminish with age and shaft vibration. However, it can be used for precision applications.
The market landscape shows the competitive environment of the gear motor industry. This report also highlights key items, income and value creation by region and country. The report also examines the competitive landscape by region, including the United States, China, India, the GCC, South Africa, Brazil, and the rest of the world. It is important to note that the report contains segment-specific information, so that readers can easily understand the market potential of the geared motors market.
Size
The safety factor, or SF, of a gear motor is an important consideration when selecting one for a particular application. It compensates for the stresses placed on the gearing and enables it to run at maximum efficiency. Manufacturers provide tables detailing typical applications, with multiplication factors for duty. A gear motor with a SF of three or more is suitable for difficult applications, while a gearmotor with a SF of one or two is suitable for relatively easy applications.
The global gear motor market is highly fragmented, with numerous small players catering to various end-use industries. The report identifies various industry trends and provides comprehensive information on the market. It outlines historical data and offers valuable insights on the industry. The report also employs several methodologies and approaches to analyze the market. In addition to providing historical data, it includes detailed information by market segment. In-depth analysis of market segments is provided to help identify which technologies will be most suitable for which applications.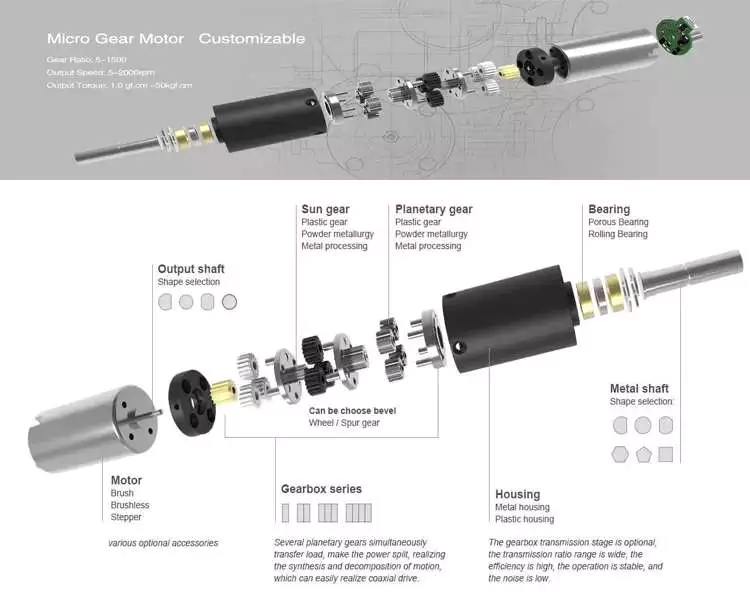
Cost
A gear motor is an electric motor that is paired with a gear train. They are available in AC or DC power systems. Compared to conventional motors, gear reducers can maximize torque while maintaining compact dimensions. But the trade-off is the reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, when used correctly, a gear motor can produce optimal output and mechanical fit. To understand how a gear motor works, let’s look at two types: right-angle geared motors and inline geared motors. The first two types are usually used in automation equipment and in agricultural and medical applications. The latter type is designed for rugged applications.
In addition to its efficiency, DC gear motors are space-saving and have low energy consumption. They can be used in a number of applications including money counters and printers. Automatic window machines and curtains, glass curtain walls, and banknote vending machines are some of the other major applications of these motors. They can cost up to 10 horsepower, which is a lot for an industrial machine. However, these are not all-out expensive.
Electric gear motors are versatile and widely used. However, they do not work well in applications requiring high shaft speed and torque. Examples of these include conveyor drives, frozen beverage machines, and medical tools. These applications require high shaft speed, so gear motors are not ideal for these applications. However, if noise and other problems are not a concern, a motor-only solution may be the better choice. This way, you can use a single motor for multiple applications.
Maintenance
Geared motors are among the most common equipment used for drive trains. Proper maintenance can prevent damage and maximize their efficiency. A guide to gear motor maintenance is available from WEG. To prevent further damage, follow these maintenance steps:
Regularly check electrical connections. Check for loose connections and torque them to the recommended values. Also, check the contacts and relays to make sure they are not tangled or damaged. Check the environment around the gear motor to prevent dust from clogging the passageway of electric current. A proper maintenance plan will help you identify problems and extend their life. The manual will also tell you about any problems with the gearmotor. However, this is not enough – it is important to check the condition of the gearbox and its parts.
Conduct visual inspection. The purpose of visual inspection is to note any irregularities that may indicate possible problems with the gear motor. A dirty motor may be an indication of a rough environment and a lot of problems. You can also perform a smell test. If you can smell a burned odor coming from the windings, there may be an overheating problem. Overheating can cause the windings to burn and damage.
Reactive maintenance is the most common method of motor maintenance. In this type of maintenance, you only perform repairs if the motor stops working due to a malfunction. Regular inspection is necessary to avoid unexpected motor failures. By using a logbook to document motor operations, you can determine when it is time to replace the gear motor. In contrast to preventive maintenance, reactive maintenance requires no regular tests or services. However, it is recommended to perform inspections every six months.


editor by CX 2023-04-24
China Hot selling DM-65SS 3530 65mm Dongming oem electric micro metal spur gearbox reducer 6v 12v 24v dc gear motor 10000rpm with high quality
Warranty: 6 months
Applicable Industries: Hotels, Garment Shops, Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms, Restaurant, Home Use, Retail, Food Shop, Printing Shops, Construction works , Energy & Mining, Food & Beverage Shops, Advertising Company
Customized support: OEM, ODM, JDM
Gearing Arrangement: Spur
Output Torque: 0.5~20kgf.cm
Input Speed: 3000~10000rpm
Output Speed: 10~200rpm
Working Current: 0.~1.0A
Gearbox Size: 65*38*H12mm
Stall Torque: 2kgf.cm-50kgf.cm
Driving Motor Speed: 3000rpm-10000rpm
Gears Style: Metal gear
Shaft diameter: 6mm
Normal Shaft Length: 24mm
Certification: CE, Rohs, CE, Factory Supply Attractive Price Big 4wheel Drive 4000w 4×4 Quad Electric Atv For Farm Rohs
Application: door lock, robotic
Working Hours: 500-800 hours
Packaging Details: Foam packed with outer paper cartons
Products Description Appearance size: Products Specification Gearbox Data:
Number of stages
3
4
5
Reduction ratio
40.5,67.5
135,225
450
Gearbox length “L”mm
12
12
12
Breaking torque(kgf.cm)
10
25
35
Gearbox efficiency
73%
65%
59%
Driving Motor Data:
Motor model
RatedVolt.
No load
Load
Stall
Current
Speed
Current
Speed
Torque
Outputpower
Torque
Current
V
mA
r/min
mA
r/min
gf.cm
W
gf.cm
mA
DM-3530-012-3000
12
≤40
3000
≤240
2200
40
0.9
≥160
≥700
DM-3530-012-4500
12
≤60
4500
≤450
3300
50
1.7
≥300
≥1400
DM-3530-012-6000
12
≤90
6000
≤700
4500
60
2.8
≥350
≥2000
DM-3530-571-3000
24
≤20
3000
≤150
2200
40
0.9
≥ JINAO SEIKI ST52 PTO Shaft Tube Seamless for Agriculture Drive Shaft 160
≥400
DM-3530-571-4500
24
≤30
4500
≤230
3300
50
1.7
≥220
≥600
DM-3530-571-6000
24
≤45
6000
≤360
4500
60
2.8
≥330
≥900
Gear Motor Data:
Motor model
RatedVolt.
No load
Load
Stall
Current
Speed
Current
Speed
Torque
Output power
Torque
Current
V
A
r/min
A
r/min
kgf.cm
W
kgf.cm
A
DM-65SS35300123000-135K
12.0
0.02
20.5
0.10
17.5
3.0
0.53
20.0
0.58
DM-65SS35300123000-152K
12.0
0.02
18.8
0.10
15.9
3.1
0.51
20.0
0.54
DM-65SS35300124500-135K
12.0
0.04
33.5
0.22
29.0
4.4
1.30
30.0
1.39
DM-65SS35300124500-152K
12.0
0.04
29.6
0.22
25.1
4.8
1.23
31.1
1.22
DM-65SS35300124500-225K
12.0
0.04
19.2
0.24
16.5
7.0
1.27
54.0
1.49
DM-65SS35300126000-225K
12.0
0.09
27.1
0.45
22.8
10.6
2.50
67.3
2.41
DM-65SS35300129500-40.5K
12.0
0.21
218.2
0.88
170.9
2.4
4.23
11.1
3.28
DM-65SS35300129500-450K
12.0
0.28
18.0
0.88
13.8
21.3
3.02
91.1
2.86
DM-65SS35305713000-450K
24.0
0.02
6.7
0.07
5.2
8.3
0.45
38.7
0.25
DM-65SS35305713500-225K
24.0
0.03
12.9
0.11
10.4
8.8
0.95
45.5
0.45
DM-65SS35305718100-450K
24.0
0.08
18.0
0.25
13.6
13.0
1.82
53.0
0.76
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis.ming Motor Co., Ltd. is specialized in designing, manufacturing and selling micro DC motors, especially gear motors.We have successfully worked out over 100 series of micro DC motors. Our products are widely applied in household appliances,audio/video products, office equipment, health-care and beauty-care facilities, medical appliances, high-class toys, electronictools, electronic commodity, Go EV Now 65130Kw RMHD4500 Multi-mode Hybrid Drive AC motor with controller gearbox for 18M BUS automotive parts and automatic systems.We have a team of professional staff who are working on R&Dand QC. They ensure our good quality managing system and advance technology.
The Parts of a Gearbox
There are many parts of a Gearbox, and this article will help you understand its functions and components. Learn about its maintenance and proper care, and you’ll be on your way to repairing your car. The complexity of a Gearbox also makes it easy to make mistakes. Learn about its functions and components so that you’ll be able to make the best choices possible. Read on to learn more. Then, get your car ready for winter!
Components
Gearboxes are fully integrated mechanical components that consist of a series of gears. They also contain shafts, bearings, and a flange to mount a motor. The terms gearhead and gearbox are not often used interchangeably in the motion industry, but they are often synonymous. Gearheads are open gearing assemblies that are installed in a machine frame. Some newer designs, such as battery-powered mobile units, require tighter integration.
The power losses in a gearbox can be divided into no-load and load-dependent losses. The no-load losses originate in the gear pair and the bearings and are proportional to the ratio of shaft speed and torque. The latter is a function of the coefficient of friction and speed. The no-load losses are the most serious, since they represent the largest proportion of the total loss. This is because they increase with speed.
Temperature measurement is another important preventive maintenance practice. The heat generated by the gearbox can damage components. High-temperature oil degrades quickly at high temperatures, which is why the sump oil temperature should be monitored periodically. The maximum temperature for R&O mineral oils is 93degC. However, if the sump oil temperature is more than 200degF, it can cause seal damage, gear and bearing wear, and premature failure of the gearbox.
Regardless of its size, the gearbox is a crucial part of a car’s drivetrain. Whether the car is a sports car, a luxury car, or a farm tractor, the gearbox is an essential component of the vehicle. There are two main types of gearbox: standard and precision. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The most important consideration when selecting a gearbox is the torque output.
The main shaft and the clutch shaft are the two major components of a gearbox. The main shaft runs at engine speed and the countershaft may be at a lower speed. In addition to the main shaft, the clutch shaft has a bearing. The gear ratio determines the amount of torque that can be transferred between the countershaft and the main shaft. The drive shaft also has another name: the propeller shaft.
The gears, shafts, and hub/shaft connection are designed according to endurance design standards. Depending on the application, each component must be able to withstand the normal stresses that the system will experience. Oftentimes, the minimum speed range is ten to twenty m/s. However, this range can differ between different transmissions. Generally, the gears and shafts in a gearbox should have an endurance limit that is less than that limit.
The bearings in a gearbox are considered wear parts. While they should be replaced when they wear down, they can be kept in service much longer than their intended L10 life. Using predictive maintenance, manufacturers can determine when to replace the bearing before it damages the gears and other components. For a gearbox to function properly, it must have all the components listed above. And the clutch, which enables the transmission of torque, is considered the most important component.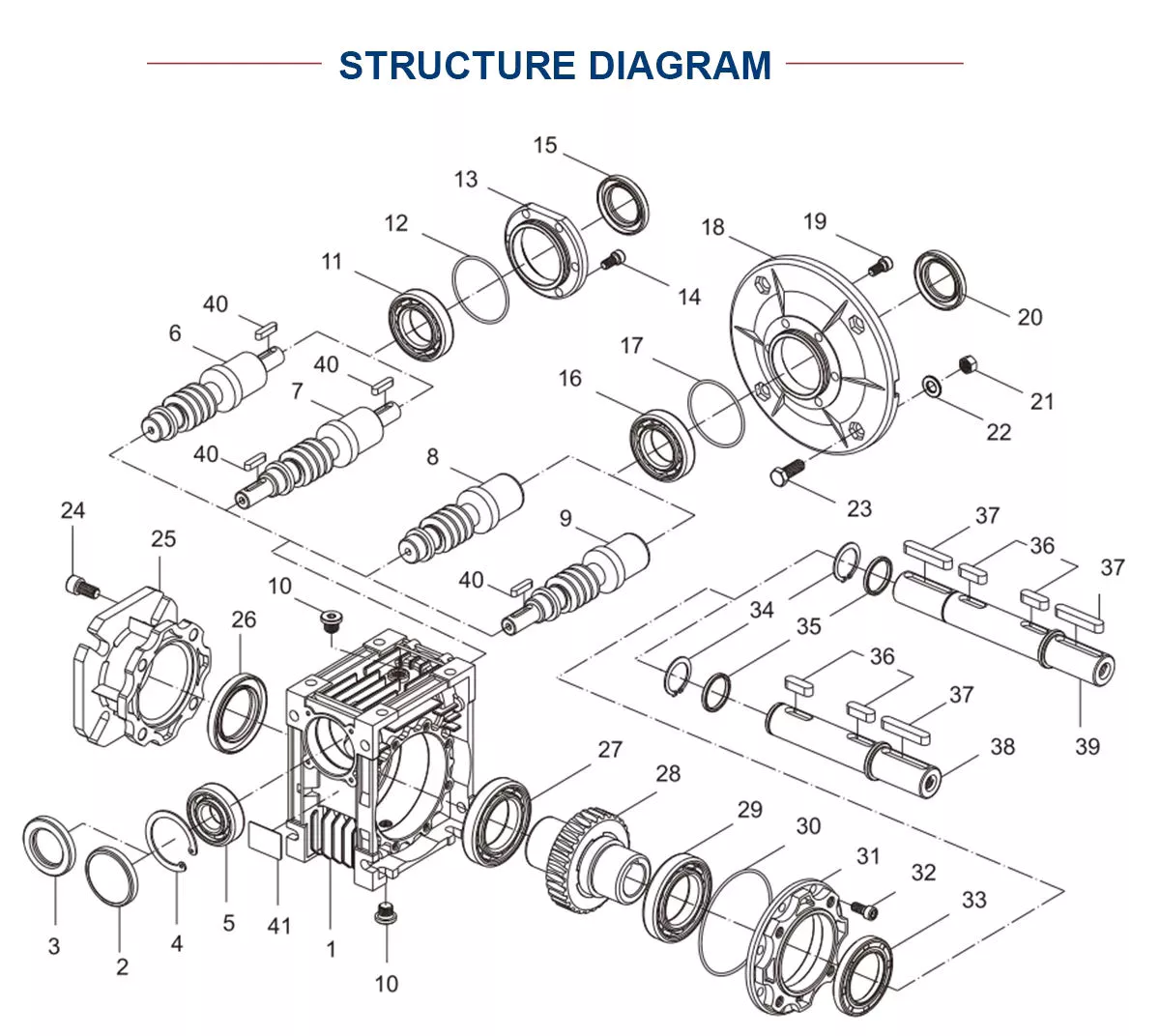
Functions
A gearbox is a fully integrated mechanical component that consists of mating gears. It is enclosed in a housing that houses the shafts, bearings, and flange for motor mounting. The purpose of a gearbox is to increase torque and change the speed of an engine by connecting the two rotating shafts together. A gearbox is generally made up of multiple gears that are linked together using couplings, belts, chains, or hollow shaft connections. When power and torque are held constant, speed and torque are inversely proportional. The speed of a gearbox is determined by the ratio of the gears that are engaged to transmit power.
The gear ratios in a gearbox are the number of steps a motor can take to convert torque into horsepower. The amount of torque required at the wheels depends on the operating conditions. A vehicle needs more torque than its peak torque when it is moving from a standstill. Therefore, the first gear ratio is used to increase torque and move the vehicle forward. To move up a gradient, more torque is required. To maintain momentum, the intermediate gear ratio is used.
As metal-to-metal contact is a common cause of gearbox failure, it is essential to monitor the condition of these components closely. The main focus of the proactive series of tests is abnormal wear and contamination, while the preventative tests focus on oil condition and additive depletion. The AN and ferrous density tests are exceptions to this rule, but they are used more for detecting abnormal additive depletion. In addition, lubrication is critical to the efficiency of gearboxes.
Maintenance
Daily maintenance is a critical aspect of the life cycle of a gearbox. During maintenance, you must inspect all gearbox connection parts. Any loose or damaged connection part should be tightened immediately. Oil can be tested using an infrared thermometer and particle counters, spectrometric analysis, or ferrography. You should check for excessive wear and tear, cracks, and oil leaks. If any of these components fail, you should replace them as soon as possible.
Proper analysis of failure patterns is a necessary part of any preventative maintenance program. This analysis will help identify the root cause of gearbox failures, as well as plan for future preventative maintenance. By properly planning preventative maintenance, you can avoid the expense and inconvenience of repairing or replacing a gearbox prematurely. You can even outsource gearbox maintenance to a company whose experts are knowledgeable in this field. The results of the analysis will help you create a more effective preventative maintenance program.
It is important to check the condition of the gearbox oil periodically. The oil should be changed according to its temperature and the hours of operation. The temperature is a significant determinant of the frequency of oil changes. Higher temperatures require more frequent changes, and the level of protection from moisture and water reduces by 75%. At elevated temperatures, the oil’s molecular structure breaks down more quickly, inhibiting the formation of a protective film.
Fortunately, the gear industry has developed innovative technologies and services that can help plant operators reduce their downtime and ensure optimal performance from their industrial gears. Here are 10 steps to ensure that your gearbox continues to serve its purpose. When you are preparing for maintenance, always keep in mind the following tips:
Regular vibration analysis is a vital part of gearbox maintenance. Increased vibration signals impending problems. Visually inspect the internal gears for signs of spiraling and pitting. You can use engineers’ blue to check the contact pattern of gear teeth. If there is a misalignment, bearings or housings are worn and need replacement. Also make sure the breathers remain clean. In dirty applications, this is more difficult to do.
Proper lubrication is another key factor in the life of gearboxes. Proper lubrication prevents failure. The oil must be free of foreign materials and have the proper amount of flow. Proper lubricant selection depends on the type of gear, reduction ratio, and input power. In addition to oil level, the lubricant must be regulated for the size and shape of gears. If not, the lubricant should be changed.
Lack of proper lubrication reduces the strength of other gears. Improper maintenance reduces the life of the transmission. Whether the transmission is overloaded or undersized, excessive vibration can damage the gear. If it is not properly lubricated, it can be damaged beyond repair. Then, the need for replacement gears may arise. However, it is not a time to waste a lot of money and time on repairs.


China Standard Low Noise Small Electric Gear Reducer Motor with Good quality
Merchandise Description
Under are only some standard types, for far more specification or a customed motor, pls speak to us.
The specification of Low sound small electric powered gear reducer motor
The drawing of Low sound modest electrical equipment reducer motor
About our organization
Probond motors designs brush, brushless, stepper, hysteresis and linear motors to fulfill consumers requirements.
Our motors use common and particular components with buyer chosen torque/speed specifications that can be modified to your purposes.
Probond motor owns skilled product sales crew and engineer group with a lot more than ten a long time expertise in motor industry, dependent on China mainland dealing with overseas organization for several years, we know your demands greater than other individuals.
Probond Sonicare Toothbrush Motor and Thermostatic Valve Hysteresis Motor are our sizzling items on market in 2017 with hugely high quality stage and competitive cost.
Conditions of Trade
Our guarantee to our Buyers:
1. Solution customer’s inquiry inside 2 working days.
2. Reply to our customer questions & Issues inside 3 functioning times.
three. Accept Consumer buy orders within 24 hrs.
Contact
Advantages of a Planetary Motor
Aside from currently being 1 of the most productive types of a generate, a Planetary Motor also gives a great amount of other benefits. These features permit it to generate a extensive assortment of equipment reductions, as nicely as generate larger torques and torque density. Let’s take a closer appear at the rewards this mechanism has to offer you. To recognize what can make it so desirable, we will discover the different types of planetary techniques.
Photo voltaic equipment
The photo voltaic equipment on a planetary motor has two distinctive advantages. It makes considerably less noise and warmth than a helical equipment. Its compact footprint also minimizes noise. It can run at high speeds without sacrificing effectiveness. However, it need to be managed with continuous treatment to work proficiently. Solar gears can be very easily destroyed by drinking water and other debris. Solar gears on planetary motors could require to be replaced more than time.
A planetary gearbox is composed of a sun gear and two or more planetary ring and spur gears. The sunlight equipment is the primary gear and is pushed by the input shaft. The other two gears mesh with the solar gear and have interaction the stationary ring equipment. The three gears are held together by a carrier, which sets the spacing. The output shaft then turns the planetary gears. This generates an output shaft that rotates.
One more gain of planetary gears is that they can transfer greater torques whilst currently being compact. These rewards have led to the generation of solar gears. They can reduce the sum of power eaten and generate more power. They also offer a longer services daily life. They are an exceptional selection for solar-driven vehicles. But they should be put in by a licensed photo voltaic energy business. And there are other advantages as nicely. When you install a photo voltaic equipment on a planetary motor, the strength developed by the solar will be converted to beneficial strength.
A solar gear on a planetary motor uses a photo voltaic equipment to transmit torque from the sun to the earth. This system performs on the principle that the solar equipment rotates at the very same charge as the world gears. The sunshine equipment has a frequent style modulus of -Ns/Np. Hence, a 24-tooth sunshine equipment equals a 3-1/2 earth equipment ratio. When you contemplate the performance of photo voltaic gears on planetary motors, you will be able to decide regardless of whether the solar gears are a lot more successful.
Solar gear
The mechanical arrangement of a planetary motor contains of two elements: a ring equipment and a sunshine gear. The ring equipment is set to the motor’s output shaft, whilst the sunshine equipment rolls around and orbits around it. The ring equipment and sun gear are connected by a planetary carrier, and the torque they make is dispersed throughout their enamel. The planetary structure arrangement also decreases backlash, and is vital to attain a swift begin and end cycle.
When the two planetary gears rotate independently, the sun gear will rotate counterclockwise and the ring-gear will turn in the very same direction. The ring-equipment assembly is mounted in a carrier. The provider equipment and sunshine gear are linked to each and every other by a shaft. The planetary gears and sun gear rotate all around every single other on the ring-gear provider to lessen the speed of the output shaft. The planetary equipment system can be multiplied or staged to acquire a greater reduction ratio.
A planetary equipment motor mimics the planetary rotation method. The input shaft turns a central equipment, recognized as the solar equipment, although the planetary gears rotate all around a stationary sunlight equipment. The motor’s compact style permits it to be very easily mounted to a motor vehicle, and its minimal weight tends to make it perfect for little cars. In addition to being very effective, a planetary gear motor also provides several other positive aspects.
A planetary gearbox makes use of a solar gear to offer torque to the other gears. The world pinions mesh with an inside tooth ring gear to make rotation. The carrier also functions as a hub amongst the input gear and output shaft. The output shaft combines these two factors, supplying a higher torque. There are a few kinds of planetary gearboxes: the sunshine equipment and a wheel travel planetary gearbox.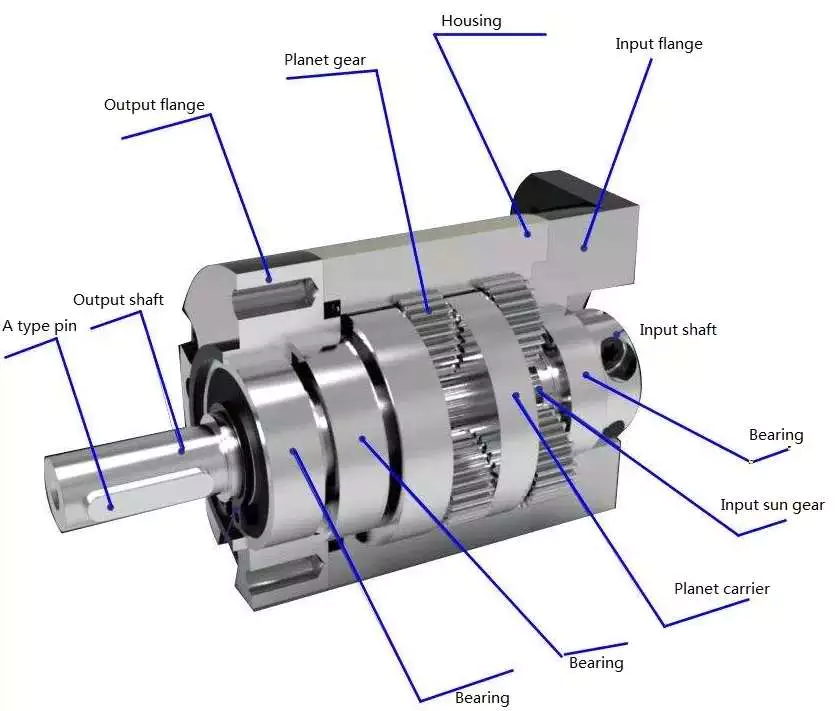
Planetary gear
A planetary motor gear functions by distributing rotational drive together a separating plate and a cylindrical shaft. A shock-absorbing gadget is incorporated among the separating plate and cylindrical shaft. This depressed part prevents abrasion use and international particles from getting into the device. The separating plate and shaft are positioned coaxially. In this arrangement, the input shaft and output shaft are rotated relative to a single one more. The rotatable disc absorbs the impact.
Yet another reward of a planetary motor gear is its performance. Planetary motor gears are extremely efficient at transferring energy, with 97% of the enter energy becoming transferred to the output. They can also have higher equipment ratios, and supply reduced sound and backlash. This style also enables the planetary gearbox to perform with electric powered motors. In addition, planetary gears also have a long services lifestyle. The performance of planetary gears is because of in part to the large variety of enamel.
Other benefits of a planetary motor gear include the simplicity of altering ratios, as effectively as the diminished protection stock. As opposed to other gears, planetary gears will not call for unique resources for modifying ratios. They are utilised in quite a few industries, and share components throughout a number of dimensions. This means that they are price-successful to produce and call for much less security stock. They can stand up to large shock and put on, and are also compact. If you might be hunting for a planetary motor gear, you’ve got arrive to the correct area.
The axial conclude surface area of a planetary gear can be worn down by abrasion with a separating plate. In addition, international particles may possibly enter the planetary gear gadget. These particles can harm the gears or even result in sound. As a end result, you ought to check out planetary gears for harm and wear. If you’re hunting for a equipment, make sure it has been thoroughly tested and installed by a specialist.
Planetary gearbox
A planetary motor and gearbox are a widespread combination of electrical and mechanical power sources. They share the load of rotation amongst several equipment enamel to increase the torque ability. This style is also far more rigid, with minimal backlash that can be as lower as 1 or two arc minutes. The benefits of a planetary gearmotor over a standard electrical motor incorporate compact measurement, substantial effectiveness, and much less risk of equipment failure. Planetary equipment motors are also much more reputable and durable than traditional electric motors.
A planetary gearbox is designed for a single stage of reduction, or a several-phase unit can be constructed with several specific cartridges. Equipment ratios may possibly also be selected according to consumer preference, either to experience mount the output stage or to use a 5mm hex shaft. For multi-phase planetary gearboxes, there are a variety of distinct alternatives obtainable. These contain higher-performance planetary gearboxes that achieve a 98% efficiency at one reduction. In addition, they are noiseless, and decrease warmth decline.
A planetary gearbox could be utilized to increase torque in a robotic or other automated method. There are diverse types of planetary equipment sets accessible, like gearboxes with sliding or rolling sections. When deciding on a planetary gearset, contemplate the environment and other elements this sort of as backlash, torque, and ratio. There are several rewards to a planetary gearbox and the positive aspects and downsides connected with it.
Planetary gearboxes are similar to individuals in a photo voltaic method. They attribute a central sun equipment in the middle, two or a lot more outer gears, and a ring equipment at the output. The planetary gears rotate in a ring-like composition around a stationary sunshine gear. When the gears are engaged, they are related by a carrier that is fixed to the machine’s shaft.
Planetary gear motor
Planetary gear motors lessen the rotational velocity of an armature by 1 or more moments. The reduction ratio is dependent on the framework of the planetary equipment system. The planetary gear device has an output shaft and an armature shaft. A separating plate separates the two. The output shaft moves in a round pattern to turn the pinion 3. When the pinion rotates to the engagement position, it is engaged with the ring equipment 4. The ring gear then transmits the rotational torque to the armature shaft. The result is that the motor cranks up.
Planetary equipment motors are cylindrical in form and are available in different energy ranges. They are normally produced of metal or brass and contain a number of gears that share the load. These motors can take care of enormous power transfers. The planetary gear push, on the other hand, needs much more elements, this kind of as a sun’s gear and a number of planetary gears. For that reason, it could not be ideal for all types of applications. Consequently, the planetary gear travel is usually employed for much more complicated devices.
Brush dusts from the electric powered motor could enter the planetary gear system and result in it to malfunction. In addition, abrasion wear on the separating plate can impact the equipment engagement of the planetary gear unit. If this occurs, the gears will not have interaction appropriately and may possibly make sound. In order to prevent this sort of a circumstance from occurring, it is critical to routinely examine planetary gear motors and their abrasion-resistant separating plates.
Planetary gear motors occur in several distinct electrical power amounts and sizes. These motors are usually cylindrical in form and are created of steel, brass, plastic, or a mix of the two supplies. A planetary gear motor can be utilised in purposes where space is an concern. This motor also allows for minimal gearings in modest areas. The planetary gearing enables for large amounts of power transfer. The output shaft dimensions is dependent on the equipment ratio and the motor pace.

